
High Voltage
Cable pooling and DTS: safe operation of high-voltage cables in the age of RES.
What is cable pooling? It is a technology that allows several RES installations, such as photovoltaic, wind or energy storage farms, to share a single connection point.
The increasing share of renewable energy sources (RES) in the energy mix is causing grid operators and investors to look for ways to efficient use of available connection capacities.
This solution makes it possible to significantly increase energy production with the same connection conditions, but at the same time puts higher requirements for high-voltage (HV) cable infrastructure. Overloading, overheating and varying load profiles are real challenges that can shorten the life of cables. In this context, the importance of DTS (Distributed Temperature Sensing) system - an advanced measurement system enabling continuous temperature monitoring of HV cables along the entire length of the route. At Ania Holding we distribute cables High Voltage and we supervise the laying of cables.
What exactly is cable pooling? - definition and basic operation
Cable pooling is a solution in which two or more RES sources share a single point of connection to the electricity grid. The most common are wind and photovoltaic farms, which have different power generation profiles - Thus, their joint operation allows a more even load on the network.
In practice, this means that energy from different sources - e.g. from a PV farm during the day and a wind farm at night - enters the grid through the same HV cable. Such a solution:
- increases connection capacity utilisation efficiency,
- limits the need for new connections,
- reduces investment costs i project implementation time.
Typical load factors for RES sources:
- increases connection capacity utilisation efficiency,
- limits the need for new connections,
- reduces investment costs i project implementation time.
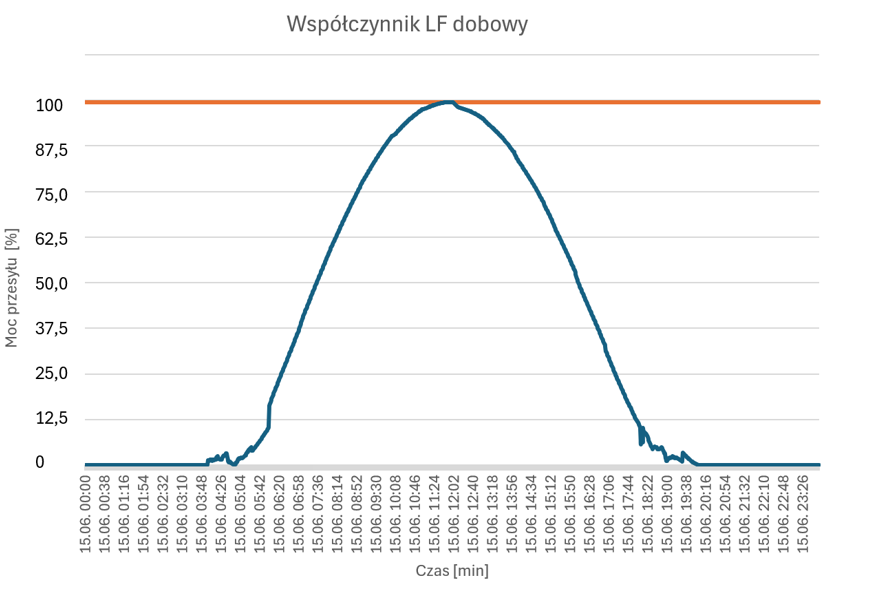
With different operating profiles, better utilisation of connection capacity can be achieved, but this means that the cable often operates close to its operating temperature limit.
Cable pooling and risk of overloading HV cables
Increased use of connection capacity is associated with cable work near maximum temperature for XLPE insulation, i.e. 90°C.
Under cable pooling conditions, HV cables are often selected „on contact” - to the connection capacity, not to the real load peaks.
Cable pooling - ways to fill the load factor:
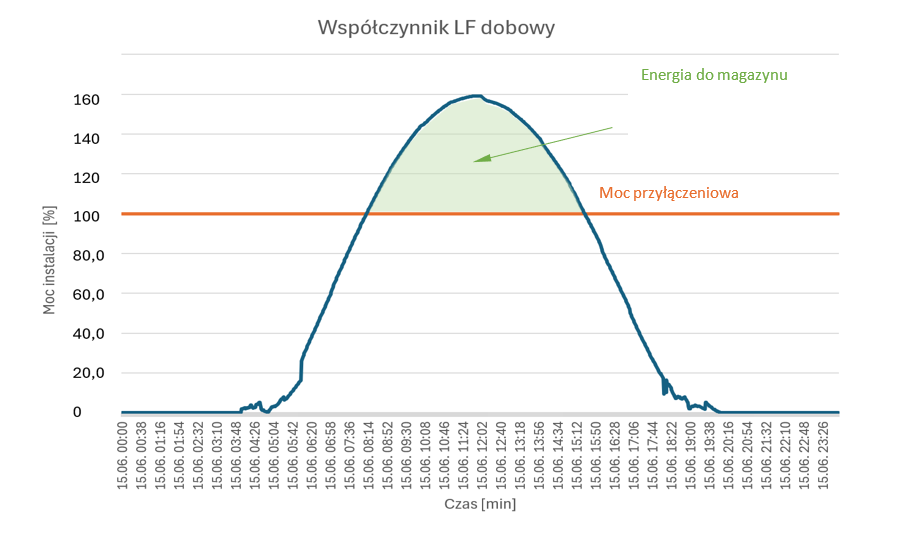
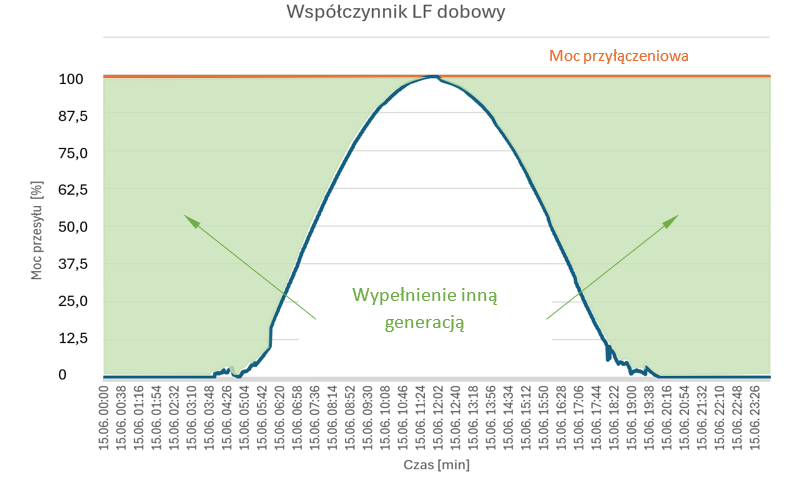
Conclusion 1:
In cable pooling systems, cable lines operate under conditions of close to the maximum permissible temperatures.
Conclusion 2:
It is easy in such situations to exceeding the long-term temperature limit for XLPE insulation (90°C), which in the long term can lead to a degradation of the insulation material and shortening the life of the cable.
How long can HV cables operate at elevated temperatures?
Operation of high voltage cables with insulation XLPE (cross-linked polyethylene) is strictly limited by temperature standards:
- Normal operating temperature: 90°C
- Emergency (short-term) temperature: 105°C
- Permissible operating time at 105°C:
- max. 72 hours per year,
- total limit for 40 years of operation: 2880 hours.
Conclusion 3:
Even if the cable system is resistant to short-term overloads, regular exceeding of temperature limits significantly reduces its service life. It is therefore crucial continuous monitoring of the HV cable temperature and rapid response to irregularities.
Overloading of cable lines - causes and effects
Overloading of HV cable lines can be divided into three main categories:
- Scheduled overloads - resulting from the network operating schedule or operator requirements, e.g. a short-term increase in energy transmission.
- External overloads - caused by environmental conditions, e.g. local variations in the ground, restriction of cable cooling, covering with a layer of material.
- Emergency overloads - the result of installation or operational errors.
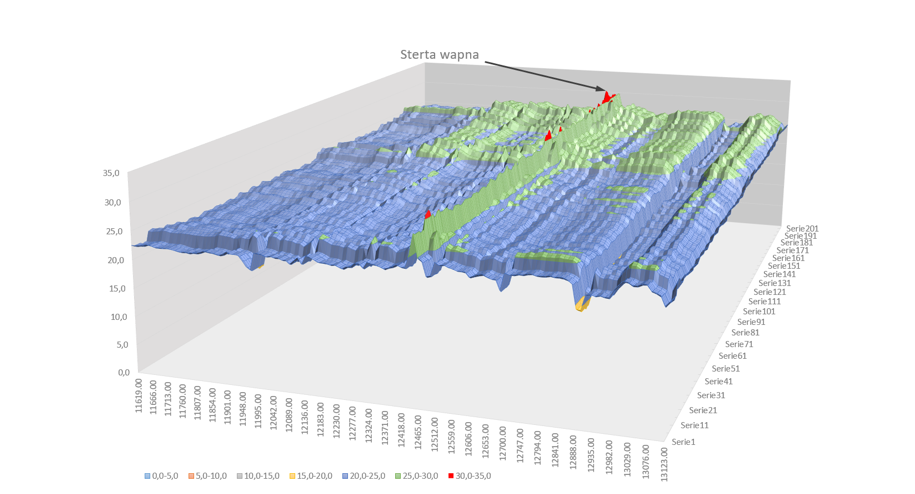
Example 1 - Hot spot caused by external factors
For example, temporary placement of a pile of lime by a farmer over the cable route can result in a localised reduction in cooling and the creation of a so-called "cooling gap". hot-spot. The temperature at a particular location rises, leading to localised overheating of the insulation.

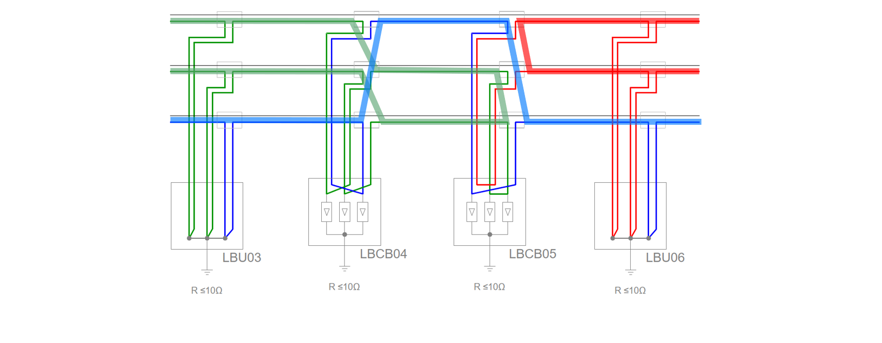
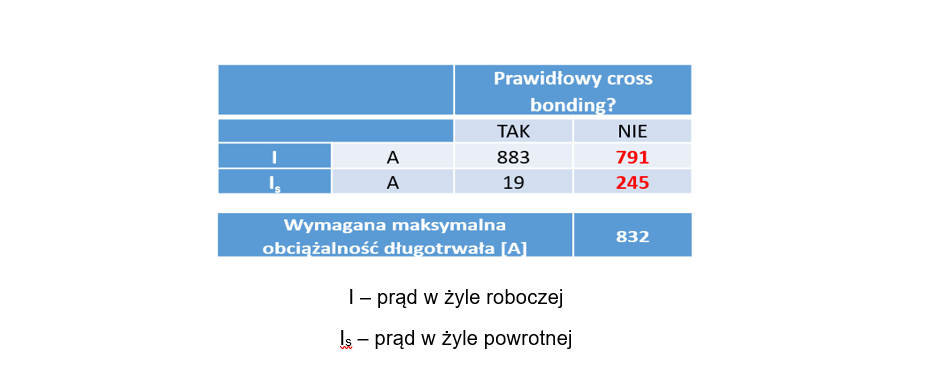
Example 2 - Wrong interleaving of return conductors
Executive error, e.g. incorrect interleaving of the return conductors, results in uneven current distribution and local overheating. The result is critical points, which can lead to damage to the cable.
The role of DTS in cable pooling protection
What is DTS (Distributed Temperature Sensing)?
System DTS is a fibre optic-based measurement solution that enables continuous and precise temperature measurement along the entire cable route.
Unlike classic point sensors, the DTS analyses the temperature along the entire length of the cable, even identifying local anomalies (hot spots).
How does DTS detect cable overheating?
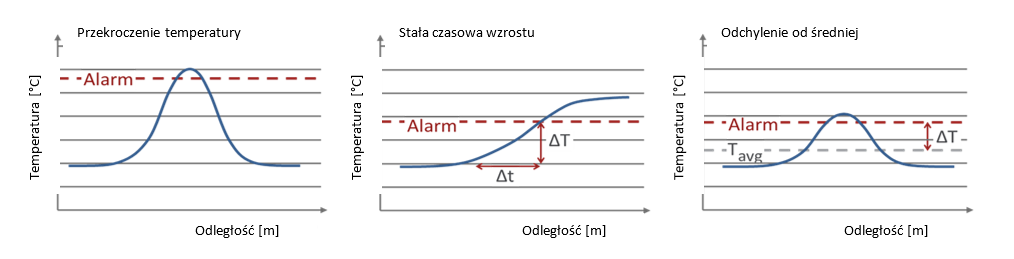
The DTS system uses temperature detection algorithms, which allow early detection of the anomaly:
- Temperature rise above setpoint - temperature alarm,
- Rate of temperature rise (time constant) - detects unnatural, rapid changes,
- Deviation from average value - indicates an abnormal behaviour of a particular section of cable.
DTS capabilities in practice
- Return line monitoring - The system measures the temperature with high resolution, detecting any thermal phenomenon in the return lines.
- Indirect RTTR surveillance - RTTR (Real-Time Thermal Rating) software analyses the load and accurately determines the temperature of the conductor, protecting the insulation from overheating.
- Analysis of the cable environment - The DTS with RTTR also monitors the ground temperature and its thermal resistivity to determine the real working conditions of the cable.
- Integration with energy management systems - The DTS can be linked to a SCADA system, allowing remote monitoring and automatic responses to temperature exceedances.
Summary - DTS as the key to safe cable pooling
Cable pooling is the future of renewable energy integration, but its successful implementation requires advanced cable line monitoring system.
Thanks to DTS system operators can:
- detect in real time overloads and hot spots,
- prevent failures and insulation degradation,
- optimise the use of infrastructure connection.
As a result, the DTS becomes not only a security tool, but also a part of a strategy to increase energy efficiency and network reliability in an era of rapidly expanding renewable energy.
recommended articles

Trade fair
Report on the thirty-eighth edition of ENERGETAB 2025
The 38th edition of the ENERGETAB International Energy Fair took place from 16-18 September 2025 in Bielsko-Biała.

Company events
A year of intensive growth for Ania Holding in energy and electrical installations
There are years that write themselves quietly, almost imperceptibly, into the history of companies. And there are those that leave a mark. The year 2025 belonged to the latter.
Company events
Ania Holding opens new regional offices
Ania Holding opens new regional offices in Gdansk and Warsaw. Closer to customers, faster response and local support for the energy industry.